Understanding Your Insurance Policy
Understanding your insurance policy can be challenging, but it’s essential to know what you’re covered for and what your responsibilities are. Here’s a guide to help break it down:
1. Types of Insurance Policies
•Health Insurance: Covers medical expenses such as hospital stays, surgeries, and prescription medications.
•Auto Insurance: Covers vehicle-related incidents like accidents, theft, and sometimes damage from natural disasters.
•Homeowners Insurance: Protects your home and personal belongings from damage or loss due to events like fires, theft, and some natural disasters.
•Life Insurance: Provides a financial payout to your beneficiaries after your death.
•Disability Insurance: Provides income if you’re unable to work due to a disability.
2. Key Components of an Insurance Policy
•Premium: The amount you pay for your insurance, usually monthly or annually.
•Deductible: The amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance starts covering costs.
•Coverage Limit: The maximum amount your insurance will pay for a claim.
•Exclusions: Specific situations or conditions that are not covered by your policy.
•Policy Term: The length of time your policy is in effect, typically one year.
3. Common Insurance Terms
•Claim: A request made to your insurance company for payment of a covered loss.
•Co-Payment (Co-pay): A fixed amount you pay for a covered service, usually in health insurance.
•Coinsurance: The percentage of costs you share with the insurance company after meeting your deductible.
•Beneficiary: The person or entity who receives the payout from a life insurance policy.
4. Reading Your Policy
•Declarations Page: This summarizes key details like coverage amounts, premiums, and deductibles.
•Insuring Agreement: Describes what is covered by the policy.
•Conditions: Lists the rules you must follow for coverage to apply (e.g., notifying the insurer of a claim within a specific timeframe).
•Endorsements: Add-ons or changes to your standard coverage that may provide additional protection.
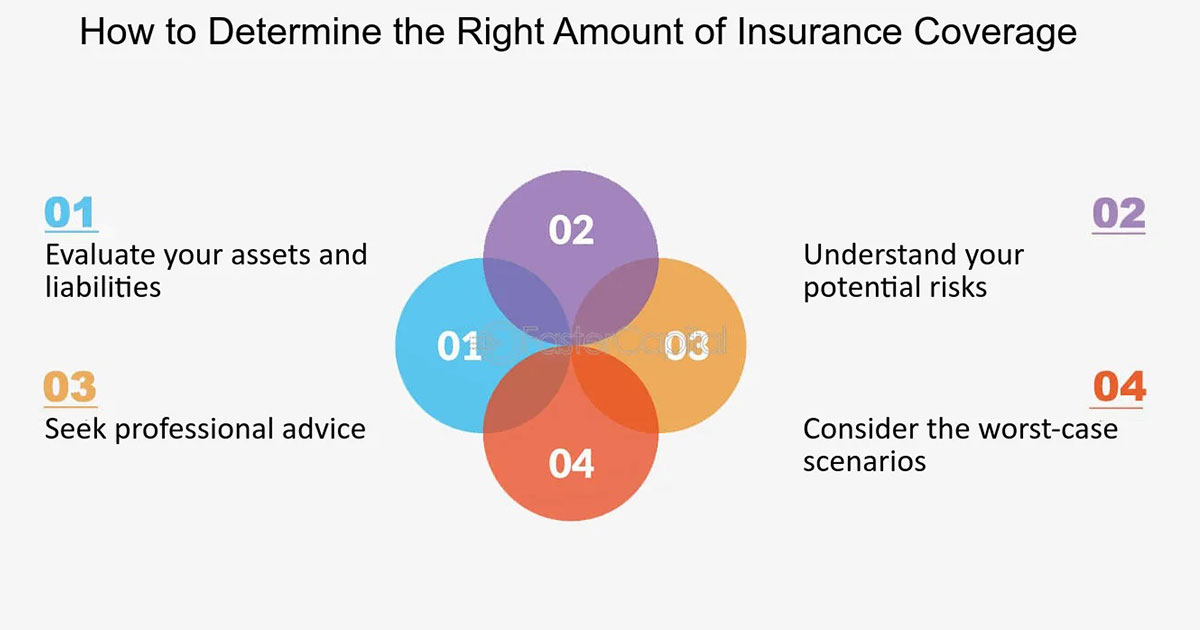
5. Tips for Managing Your Policy
•Review Annually: Ensure your coverage is still adequate, especially if you’ve had major life changes.
•Know Your Exclusions: Be aware of what isn’t covered to avoid surprises.
•Compare Policies: Shop around for better rates or coverage if necessary.
Why Review Your Policy Annually?
1. Life Changes: Significant events like marriage, having children, buying a home, or changing jobs can affect your insurance needs. Your coverage should reflect your current situation.
•Example: If you bought a new car or added an addition to your home, you may need to adjust your auto or homeowners insurance.
2. Adjust Coverage Limits: Over time, the value of your possessions or income may increase, meaning your coverage may need to be higher.
•Example: If you’ve acquired valuable assets like jewelry or electronics, you might need additional coverage.
3. Rate Comparison: Premium rates can fluctuate yearly based on changes in the insurance market or your personal situation. Comparing rates from other insurers may save you money.
•Example: You may find that switching providers gives you better coverage at a lower price.
4. Identify Redundancies: Some coverage might overlap with other policies, like having roadside assistance through both your auto insurance and credit card. An annual review helps identify and remove such redundancies.
5. Understand New Exclusions: Sometimes insurers update policy exclusions or terms. Reviewing your policy ensures you’re aware of any changes.
•Example: Your homeowners policy may no longer cover flooding, requiring you to buy additional flood insurance.
6. Discount Opportunities: Your insurer may offer discounts for changes in your situation, such as installing a home security system or completing a defensive driving course.
How to Review Your Policy Annually
1. Review the Declarations Page: This page summarizes key details like your premium, coverage limits, and deductibles. Check if these still make sense for your needs.
2. Check Coverage for Major Life Changes:
•Health Insurance: Did you change jobs, get married, or have children? Make sure your health insurance covers your family.
•Auto Insurance: Did you move to a new location or buy a new vehicle? Your rates and coverage may need adjusting.
•Homeowners Insurance: Have you made home improvements or acquired valuable items? You may need to update your policy.
•Life Insurance: Have your dependents or financial obligations changed? You might need more or less life insurance coverage.
3. Talk to Your Agent or Provider: Discuss your current situation with your agent to see if there are coverage adjustments or discounts available.
4. Compare Rates: Use online tools or work with an insurance broker to get quotes from different providers. If you find better rates, consider switching providers.
5. Review Deductibles: Make sure your deductible (the amount you pay before insurance kicks in) still fits your financial situation. Raising it may lower your premium, but make sure you can afford it if needed.
6. Ensure Adequate Liability Coverage: For auto and homeowners insurance, confirm that your liability limits are high enough to protect your assets in case of a lawsuit.